What is a Joint Arthroscopy
Joint arthroscopy is a surgical procedure that is utilized to visualize the interior of joints in different parts of the body. It is performed using tiny cameras that are passed through the skin through small incisions around the joint. Joint arthroscopy procedures can be performed for almost any joint in the body, though they are commonly performed in the knee and hip joints.
When is Joint Arthroscopy Performed?
Joint arthroscopy may be performed as an investigative procedure when attempting to make a diagnosis of a clinical condition that may be affecting the joint. It is also utilized as a treatment to remove damaged cartilage or loosen bone that may be floating around within the joint.
How is the Procedure Performed?
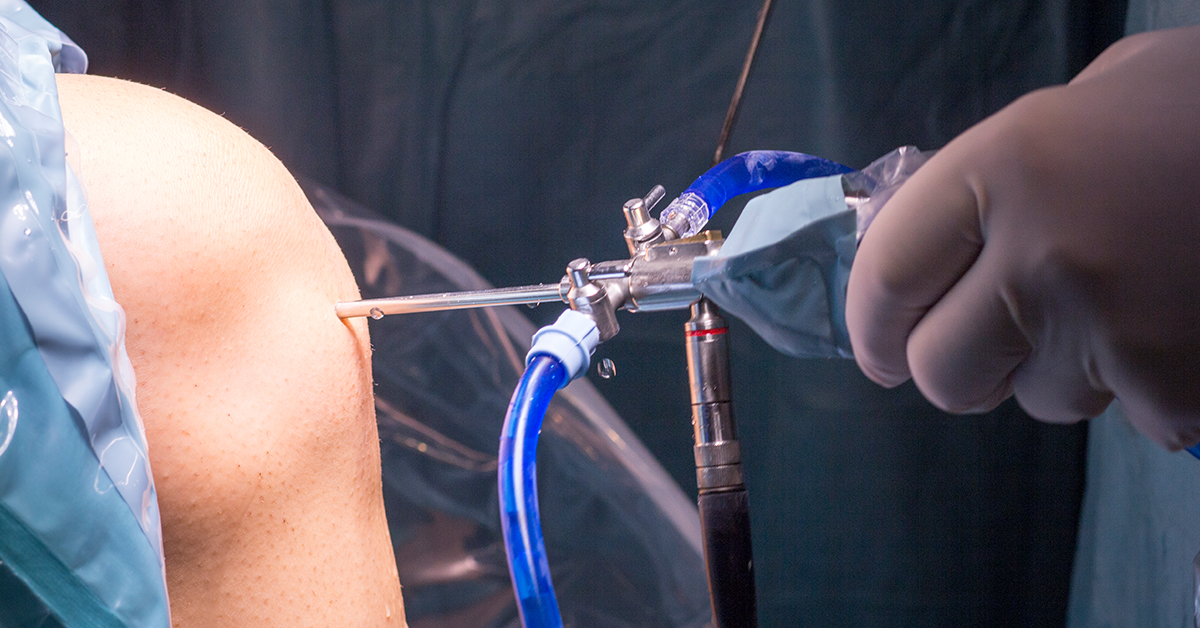
The joint arthroscopy is a fairly straightforward procedure. The procedure uses equipment called an arthroscope which is a small tube that contains fiber-optic cables within and has a light source at the tip that helps the physician visualize the structures within the joint.
Joint arthroscopy procedures are often performed as a same day case procedure. Patients only require a local anesthetic and mild sedation in most cases. Once consent has been obtained, the area where the arthroscopy is to be performed is cleaned with antiseptic solution. Small incisions are made on the skin after local anesthetic has been administered to numb it.
A small amount of sterile solution may be injected into the joint using a needle and syringe so as to expand the joint. This may feel a bit uncomfortable but is required as it allows better visualization of the structures through the arthroscope. The instruments are inserted into the joint and the images that are seen by the physician are also seen on a monitor.
Once the required images have been taken, additional instruments may be inserted if any intervention is required. Once this has concluded, the instruments are removed and the excess sterile solution that had been injected previously is withdrawn. The skin is covered with a sterile bandage and the patient is discharged home.
After the Procedure
It is not uncommon for patients to experience mild discomfort in the joint following arthroscopy. If required, icepack application and painkillers may be prescribed. Patients are requested to keep the dressings dry to allow the incisions to heal. They can return to their normal activities within 4 to 6 weeks if they have undergone surgical intervention through the arthroscope.
Benefits and Risks
The main benefit of joint arthroscopy is that it is minimally invasive and a lot can be done through just a small incision. Not only is it useful as a diagnostic tool but it also helps in treating any joint problems.
The risks are minimal and may occur if a patient has undergone general anesthesia. Mild bruising and pain at the site of the arthroscopy is common and passes after a few days. Infections are rare as the procedure is performed under sterile conditions but can be easily treated with antibiotics.

