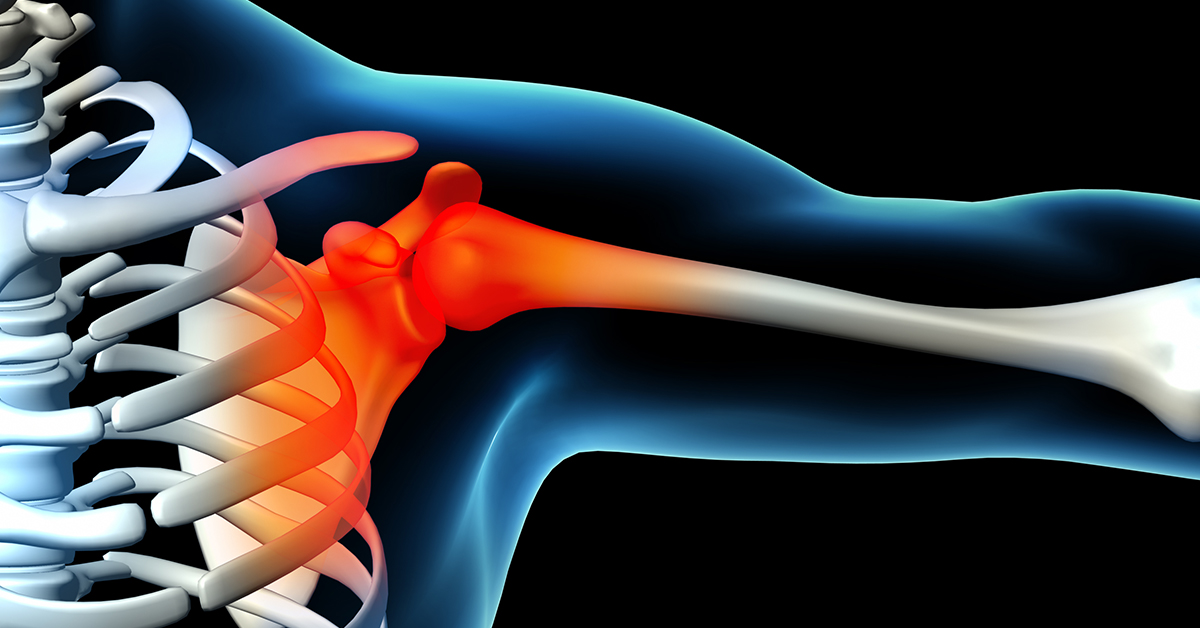
What are Glenoid Labrum Tears?
The glenohumeral joint provides most of the movement in the shoulder, and is often referred to as the shoulder joint, but there are two other joints in the shoulder. In the glenohumeral joint, the humerus head is covered with smooth cartilage so that movement is possible with as little friction as possible. The rim of the glenoid, where the humerus head is socketed, is rimmed with a ring of fibrous cartilage called the labrum. The labrum serves to help with stability in the shoulder joint by deepening the socket the humerus head nestles in. When this cartilage is torn, it is called a glenoid labrum tear.
What causes Glenoid Labrum Tears?
Glenoid labrum tears can occur from traumatic injury, like a fall or sudden impact to the shoulder. Overuse of the shoulder, which can occur in athletes or those whose work requires repetitive overhead movement, can also tear the glenoid labrum.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
One of the responsibilities of the glenoid labrum in the shoulder is to keep the shoulder stable, so symptoms of glenoid labrum tears often include feeling a loss of stability and strength in the shoulder. Other symptoms that may be present include mobility issues, pain, and sensations of grinding, popping or clicking. If your doctor determines these symptoms are present after a physical exam, you may be diagnosed with this condition. Use of imaging studies like MRI or CT scan may confirm the diagnosis, but arthroscopic surgery may be necessary to determine the extent of the damage and the best course of treatment.
How are Glenoid Labrum Tears Treated?
Conservative treatment methods may prove to be effective if the condition is not severe. These treatments include physical therapy, rest, and medication to reduce inflammation. However, if the condition is severe or does not respond to conservative methods, surgery may be beneficial.

